1. Javascript Comments
2. JavaScript Variables and Datatypes
3. Escaping Literal Quotes
4. Escape Sequences in Strings
5. Constructing Strings with Variables
6. Find the Length of a String
7. Find First Character in a String
8. Find the Nth Character in a String
9. Find the Last Character in a String
10. JavaScript Arrays
11. Nested Arrays (multi-dimensional array)
12. Access Array Data with Indexes
13. Modify Array Data with Indexes
14. Access Multi-Dimensional Arrays
15. Manipulate Arrays With push()
16. Manipulate Arrays With pop()
17. Manipulate Arrays With shift()
18. Manipulate Arrays With unshift()
19. JavaScript Functions
20. Functions with Arguments
21. Assignment with a Returned Value
22. If Statements
23. Logical And Operator
24. Logical Or Operator
25. Else If Statements
26. Switch Statements
27. Identical Options in Switch Statements
28. Simplified Boolean Functions
29. JavaScript Objects
30. Accessing Object Properties
31. Updating Object Properties
32. Adding New Properties to Object
33. Delete Properties from Object
34. Using Objects for Lookups
35. Checking Objects for Properties
36. Accessing Nested Objects
37. Accessing Nested Arrays
38. While Loops
39. For Loops
40. For Loops - Odd Numbers
41. For Loops - Odd Numbers Backwards
42. For Loops - Arrays
43. Nesting For Loops
44. Do...While Loops
45. Recursions
46. Generate Random Numbers
47. Generate Random Numbers within a Range
48. ParseInt Function
49. ParseInt Function with Radix
50. Ternary Operator
51. Multiple Ternary Operators
52. Recursion for Countdown
53. Recursion for Range of Numbers
1. Javascript Comments
>>Return to Menu
// This is an in-line comment.
/* This is a
multi-line comment */
2. JavaScript Variables and Datatypes
>>Return to Menu
These are some of the Javascript DataTypes:
- undefined
- null
- boolean
- string
- symbol
- bigint
- number
- object
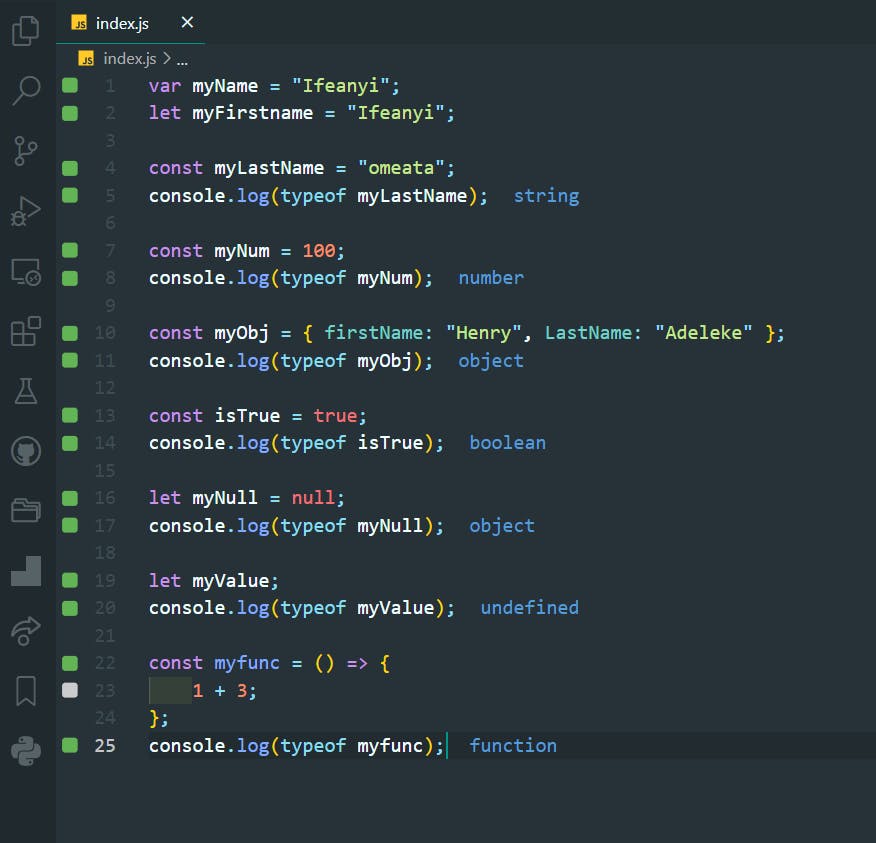
var myName = "Ifeanyi";
let myFirstname = "Ifeanyi";
const myLastName = "omeata";
console.log(typeof myLastName);
const myNum = 100;
console.log(typeof myNum);
const myObj = { firstName: "Henry", LastName: "Adeleke" };
console.log(typeof myObj);
const isTrue = true;
console.log(typeof isTrue);
let myNull = null;
console.log(typeof myNull);
let myValue;
console.log(typeof myValue);
const myfunc = () => {
1 + 3;
};
console.log(typeof myfunc);
3. Escaping Literal Quotes
>>Return to Menu
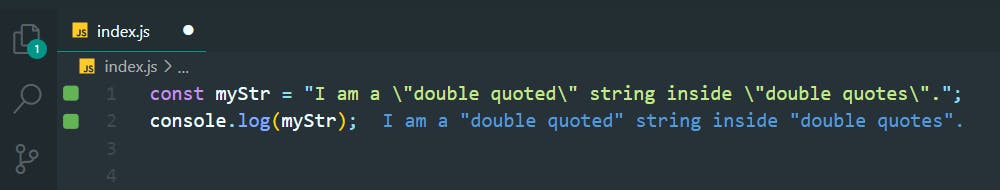
const myStr = "I am a \"double quoted\" string inside \"double quotes\".";
console.log(myStr);
4. Escape Sequences in Strings
>>Return to Menu
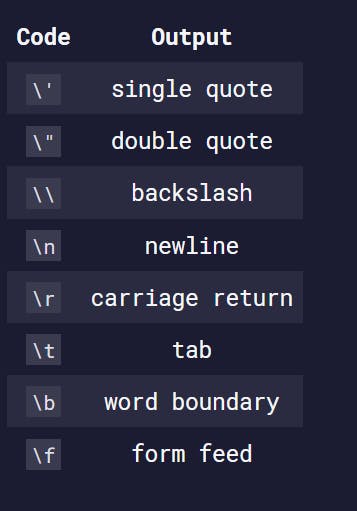
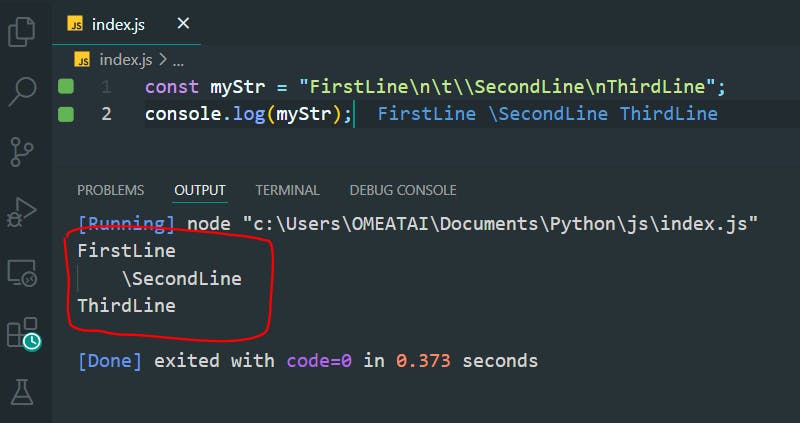
const myStr = "FirstLine\n\t\\SecondLine\nThirdLine";
console.log(myStr);
5. Constructing Strings with Variables
>>Return to Menu
const myName = "Ifeanyi";
const myStr = "My name is " + myName + " and I am well!";
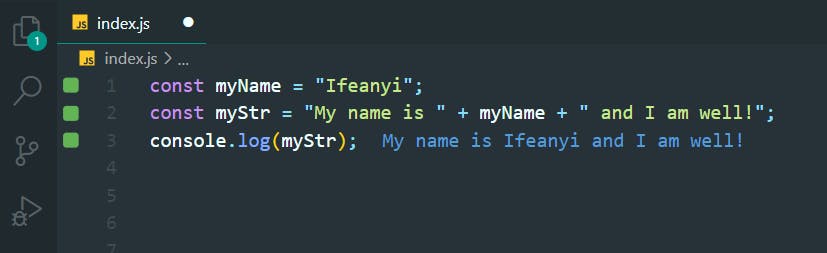
6. Find the Length of a String
>>Return to Menu
let lastNameLength = 0;
const lastName = "YellowSun";
lastNameLength = lastName.length;
console.log(lastNameLength);
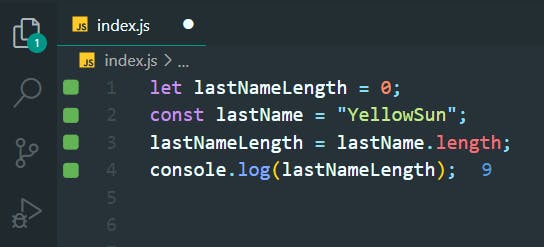
7. Find First Character in a String
>>Return to Menu
const firstName = "Charles";
const firstLetter = firstName[0];
console.log(firstLetter)
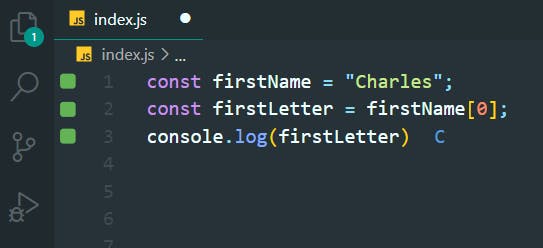
8. Find the Nth Character in a String
>>Return to Menu
const lastName = "Daniels";
const thirdLetterOfLastName = lastName[2];
console.log(thirdLetterOfLastName);
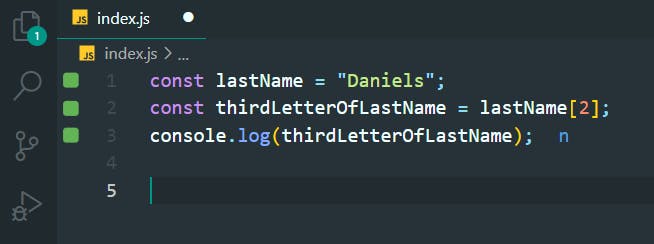
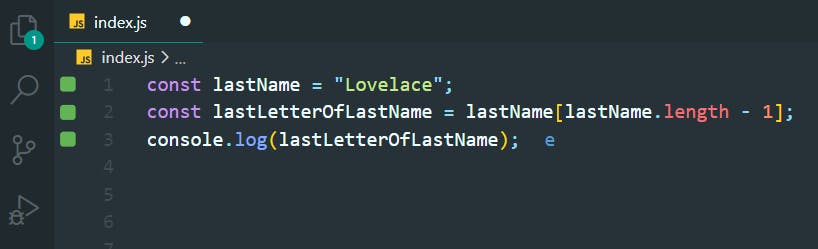
9. Find the Last Character in a String
>>Return to Menu
const lastName = "Lovelace";
const lastLetterOfLastName = lastName[lastName.length - 1];
console.log(lastLetterOfLastName);
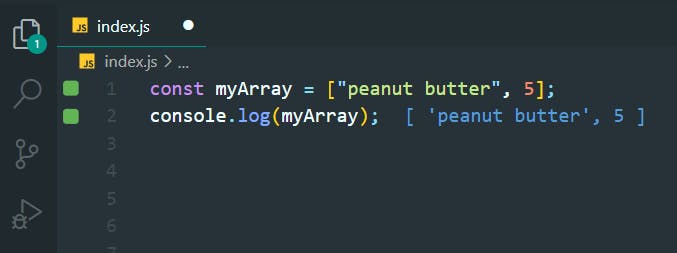
10. JavaScript Arrays
>>Return to Menu
const myArray = ["peanut butter", 5];
console.log(myArray);
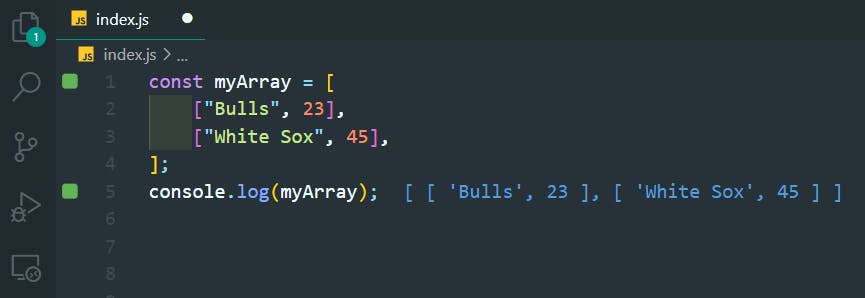
11. Nested Arrays (multi-dimensional array)
>>Return to Menu
const myArray = [
["Bulls", 23],
["White Sox", 45],
];
console.log(myArray);
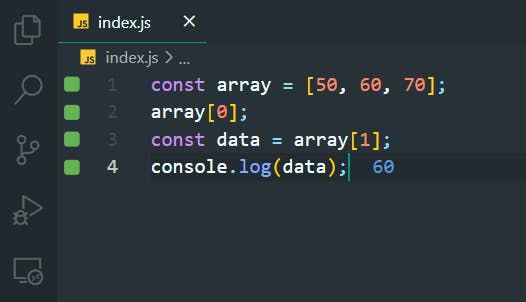
12. Access Array Data with Indexes
>>Return to Menu
const array = [50, 60, 70];
array[0];
const data = array[1];
console.log(data);
13. Modify Array Data with Indexes
>>Return to Menu
const ourArray = [50, 40, 30];
ourArray[0] = 15;
console.log(ourArray);
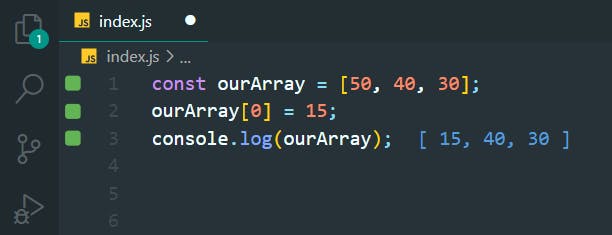
14. Access Multi-Dimensional Arrays
>>Return to Menu
const myArray = [
[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6],
[7, 8, 9],
[
[10, 11, 12], 13, 14
],
];
const myData = myArray[2][1];
console.log(myData);
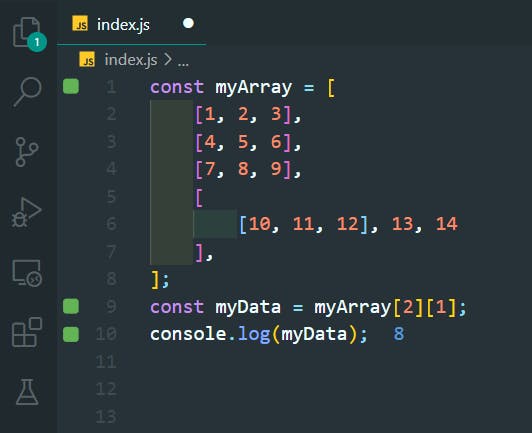
15. Manipulate Arrays With push()
>>Return to Menu
const arr1 = [1, 2, 3];
arr1.push(4);
const arr2 = ["Stimpson", "J", "cat"];
arr2.push(["happy", "joy"]);
console.log(arr1);
console.log(arr2);
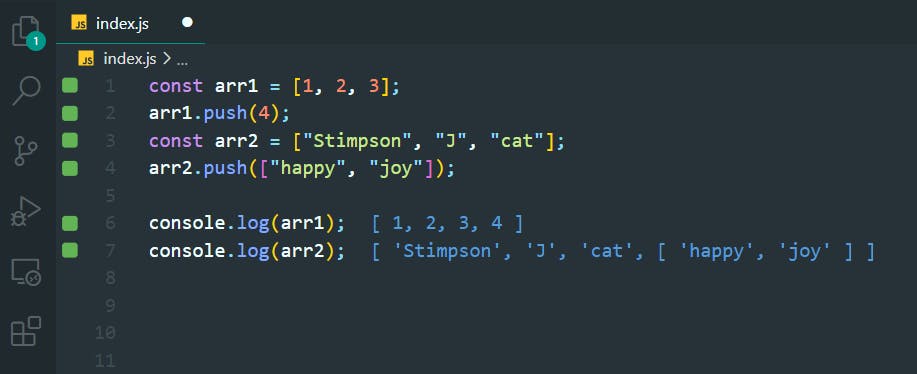
16. Manipulate Arrays With pop()
>>Return to Menu
const myArray = [["John", 23], ["cat", 2]];
const removedFromMyArray = myArray.pop()
console.log(removedFromMyArray);
console.log(myArray);
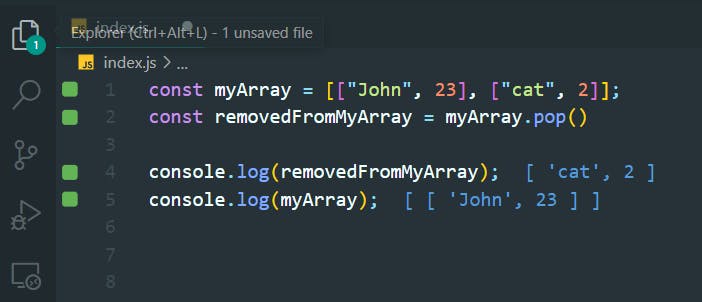
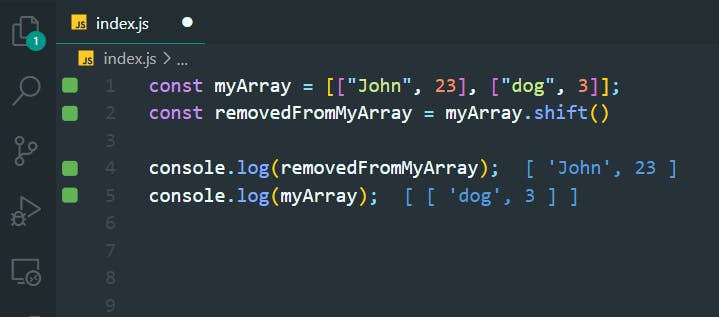
17. Manipulate Arrays With shift()
>>Return to Menu
const myArray = [["John", 23], ["dog", 3]];
const removedFromMyArray = myArray.shift()
console.log(removedFromMyArray);
console.log(myArray);
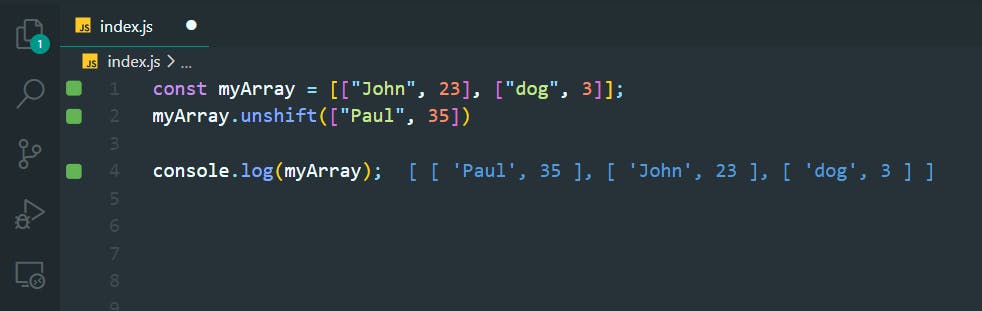
18. Manipulate Arrays With unshift()
>>Return to Menu
const myArray = [["John", 23], ["dog", 3]];
myArray.unshift(["Paul", 35])
console.log(myArray);
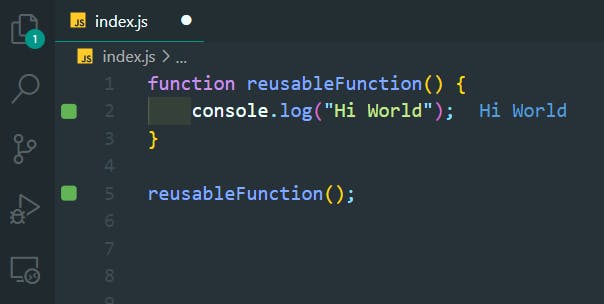
19. JavaScript Functions
>>Return to Menu
function reusableFunction() {
console.log("Hi World");
}
reusableFunction();
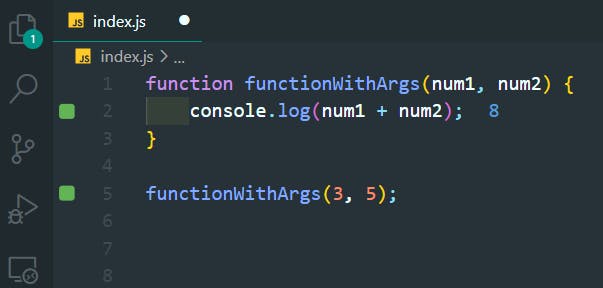
20. Functions with Arguments
>>Return to Menu
function functionWithArgs(num1, num2) {
console.log(num1 + num2);
}
functionWithArgs(3, 5);
21. Assignment with a Returned Value
>>Return to Menu
function timesFive(num) {
return num * 5;
}
console.log(timesFive(6));
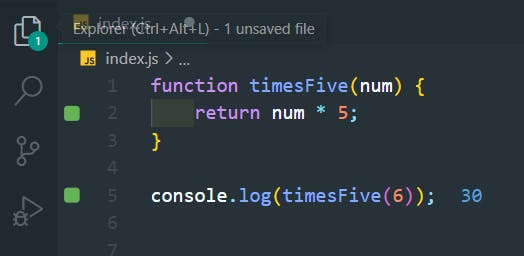
22. If Statements
>>Return to Menu
function trueOrFalse(isTrue) {
if (isTrue) {
return "Yes, It is true";
} else {
return "No, It is false";
}
}
console.log(trueOrFalse(1 < 5));
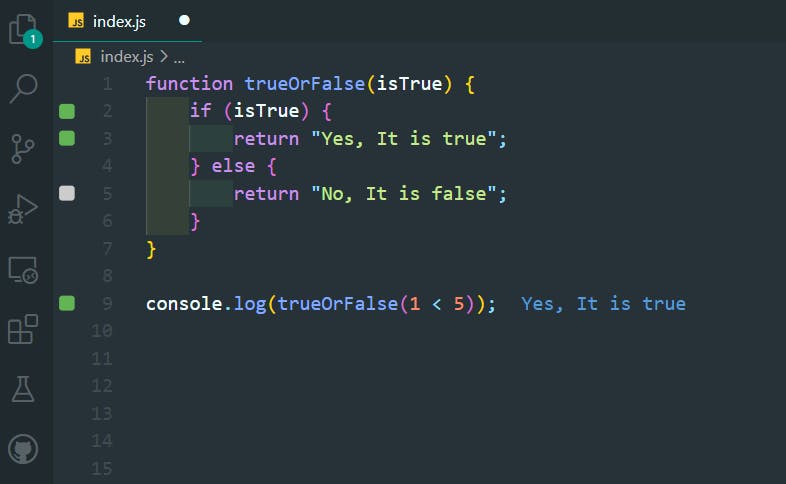
23. Logical And Operator
>>Return to Menu
function myFunc(num) {
if (num >= 5 && num <= 10) {
return "Yes";
}
return "No";
}
console.log(myFunc(9));
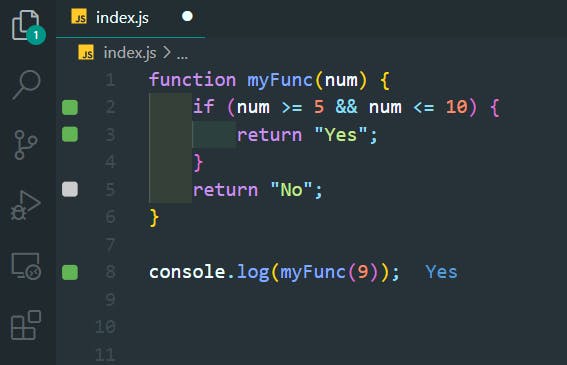
24. Logical Or Operator
>>Return to Menu
function myFunc(val) {
if (val < 10 || val > 20) {
return "Outside";
}
return "Inside";
}
console.log(myFunc(5));
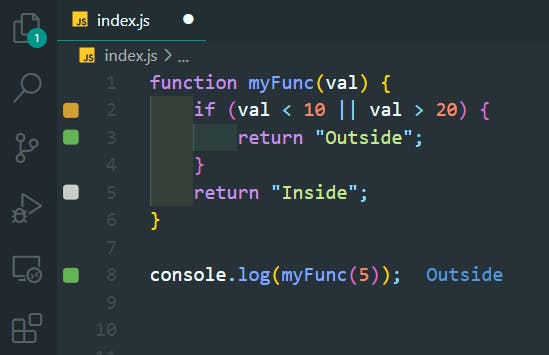
25. Else If Statements
>>Return to Menu
function testElseIf(val) {
if (val > 10) {
return "Greater than 10";
} else if (val < 5) {
return "Smaller than 5";
} else {
return "Between 5 and 10";
}
}
console.log(testElseIf(7));
26. Switch Statements
>>Return to Menu
function caseInSwitch(val) {
let answer = "";
switch (val) {
case 1:
answer = "alpha";
break;
case 2:
answer = "beta";
break;
case 3:
answer = "gamma";
break;
case 4:
answer = "delta";
break;
default:
answer = "zeta";
break;
}
return answer;
}
console.log(caseInSwitch(1));
27. Identical Options in Switch Statements
>>Return to Menu
function sequentialSizes(val) {
let answer = "";
switch (val) {
case 1:
case 2:
case 3:
answer = "Low";
break;
case 4:
case 5:
case 6:
answer = "Mid";
break;
case 7:
case 8:
case 9:
answer = "High";
break;
}
return answer;
}
console.log(sequentialSizes(4));
28. Simplified Boolean Functions
>>Return to Menu
function isEqual(a, b) {
if (a === b) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
Is same as:
function isEqual(a, b) {
return a === b;
}
29. JavaScript Objects
>>Return to Menu
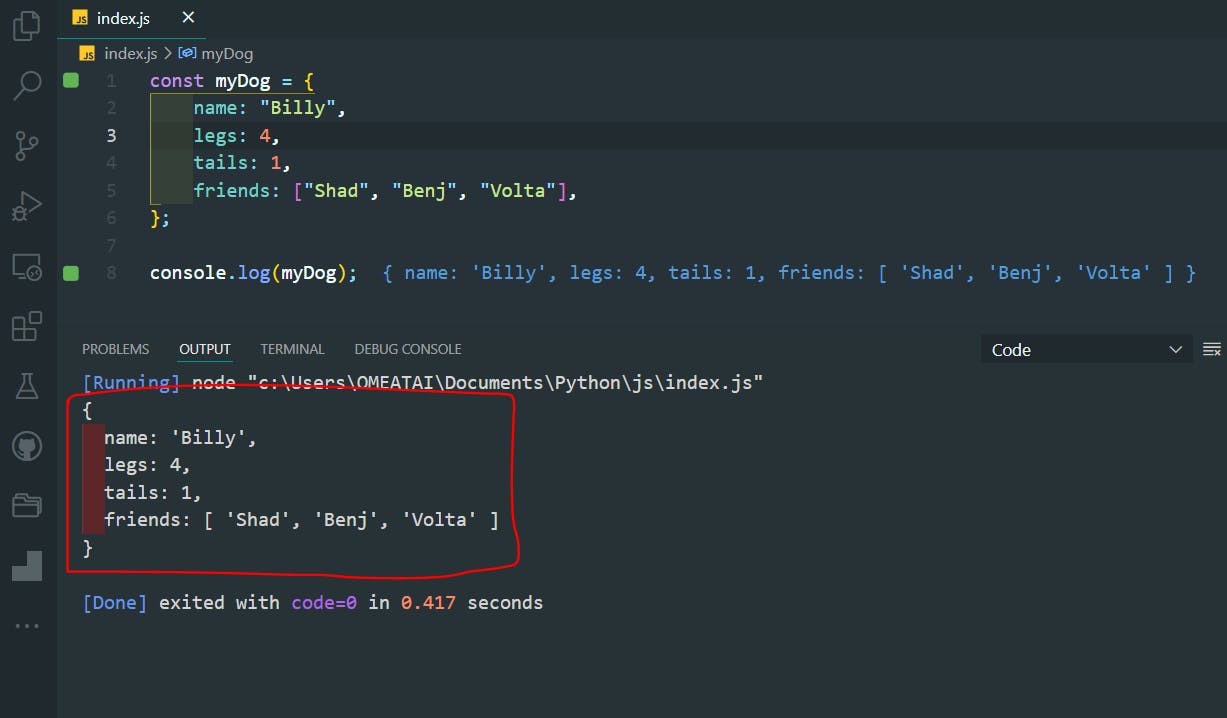
const myDog = {
name: "Billy",
legs: 4,
tails: 1,
friends: ["Shad", "Benj", "Volta"],
};
console.log(myDog);
30. Accessing Object Properties
>>Return to Menu
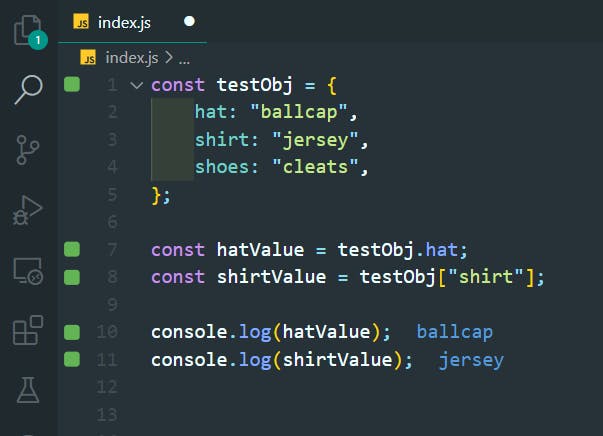
const testObj = {
hat: "ballcap",
shirt: "jersey",
shoes: "cleats",
};
const hatValue = testObj.hat;
const shirtValue = testObj["shirt"];
console.log(hatValue);
console.log(shirtValue);
31. Updating Object Properties
>>Return to Menu
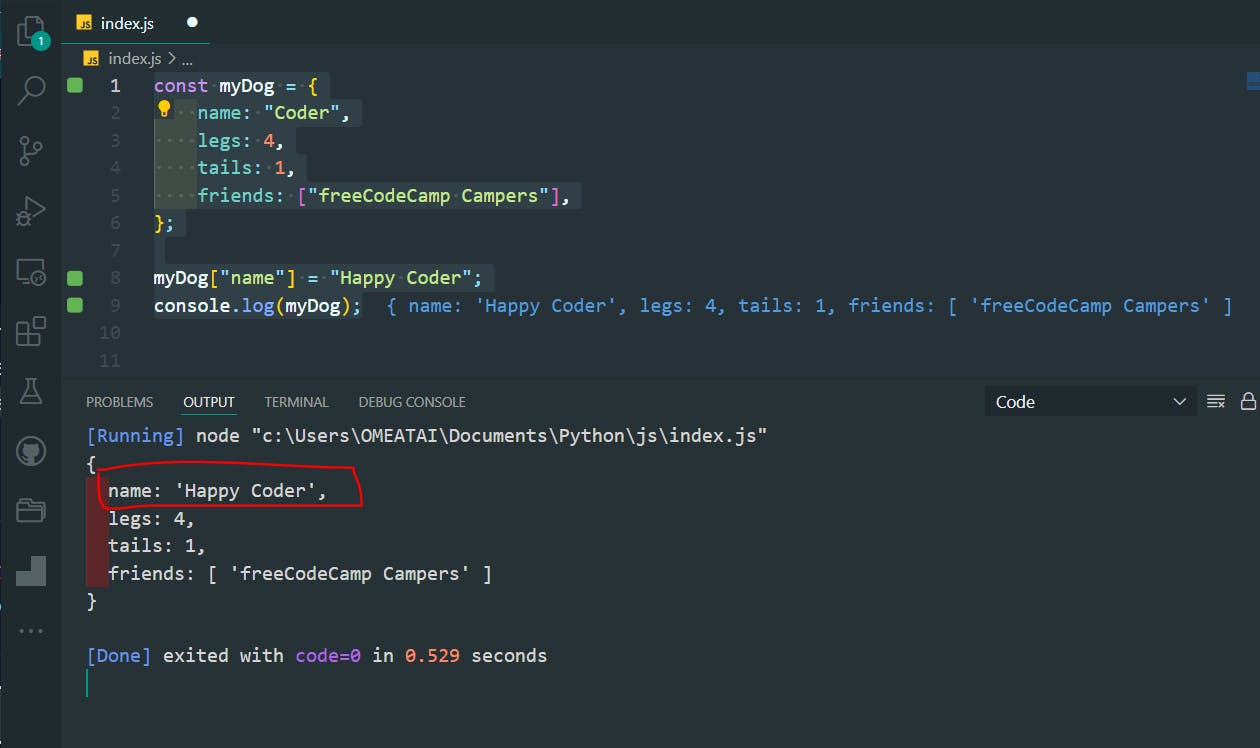
const myDog = {
name: "Coder",
legs: 4,
tails: 1,
friends: ["freeCodeCamp Campers"],
};
myDog["name"] = "Happy Coder";
console.log(myDog);
32. Adding New Properties to Object
>>Return to Menu
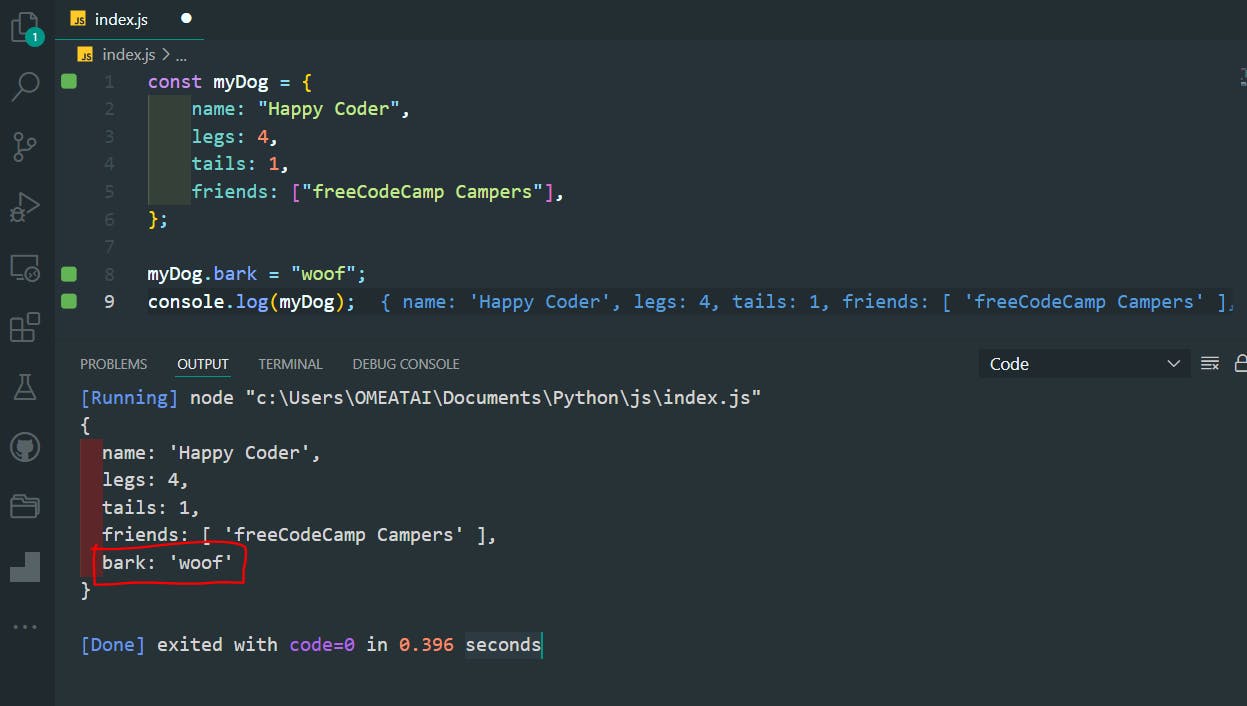
const myDog = {
name: "Happy Coder",
legs: 4,
tails: 1,
friends: ["freeCodeCamp Campers"],
};
myDog.bark = "woof";
console.log(myDog);
33. Delete Properties from Object
>>Return to Menu
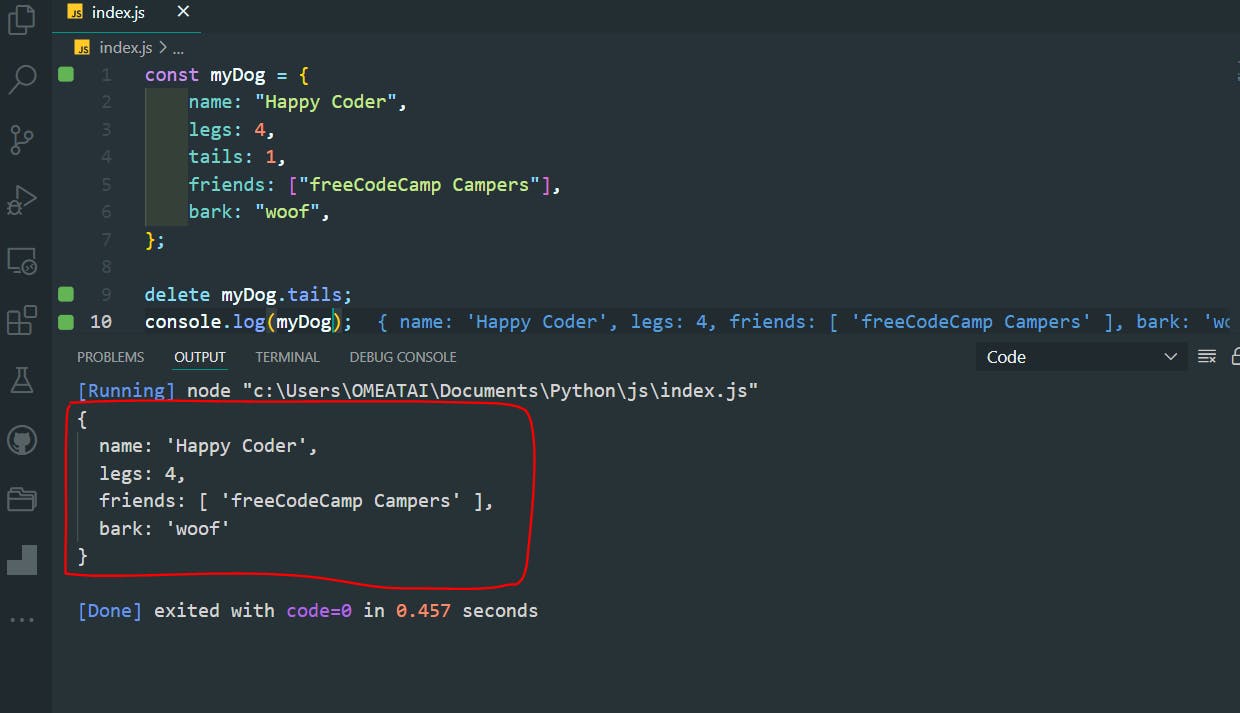
const myDog = {
name: "Happy Coder",
legs: 4,
tails: 1,
friends: ["freeCodeCamp Campers"],
bark: "woof",
};
delete myDog.tails;
console.log(myDog);
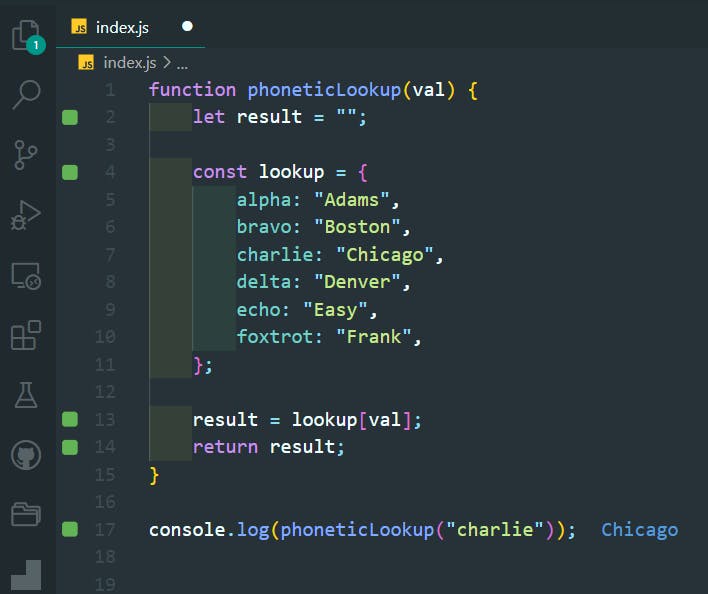
34. Using Objects for Lookups
>>Return to Menu
function phoneticLookup(val) {
let result = "";
const lookup = {
alpha: "Adams",
bravo: "Boston",
charlie: "Chicago",
delta: "Denver",
echo: "Easy",
foxtrot: "Frank",
};
result = lookup[val];
return result;
}
console.log(phoneticLookup("charlie"));
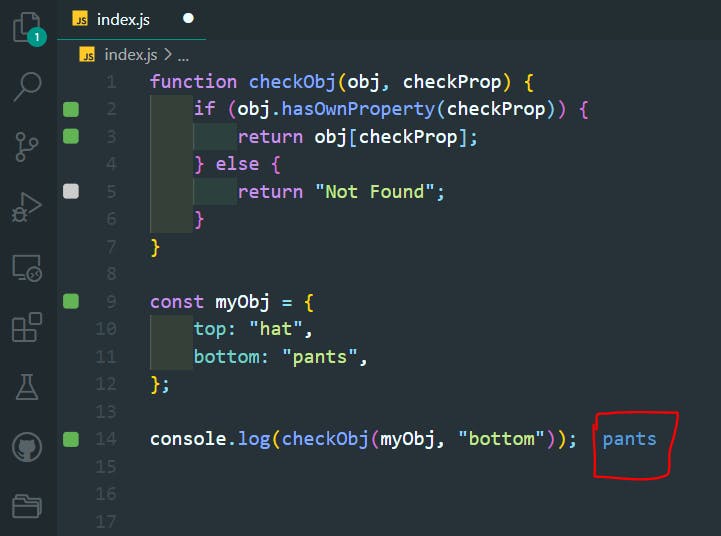
35. Checking Objects for Properties
>>Return to Menu
function checkObj(obj, checkProp) {
if (obj.hasOwnProperty(checkProp)) {
return obj[checkProp];
} else {
return "Not Found";
}
}
const myObj = {
top: "hat",
bottom: "pants",
};
console.log(checkObj(myObj, "bottom"));
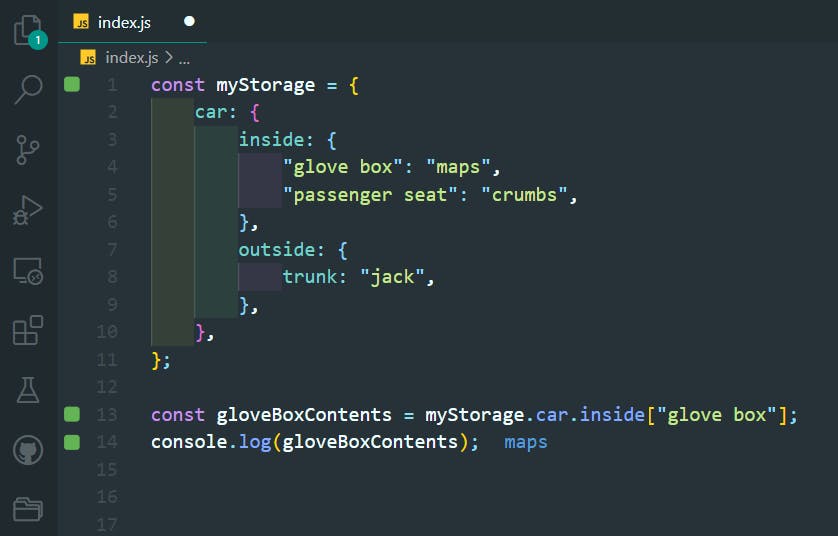
36. Accessing Nested Objects
>>Return to Menu
const myStorage = {
car: {
inside: {
"glove box": "maps",
"passenger seat": "crumbs",
},
outside: {
trunk: "jack",
},
},
};
const gloveBoxContents = myStorage.car.inside["glove box"];
console.log(gloveBoxContents);
37. Accessing Nested Arrays
>>Return to Menu
const myPlants = [{
type: "flowers",
list: ["rose", "tulip", "dandelion"],
},
{
type: "trees",
list: ["fir", "pine", "birch"],
},
];
const secondTree = myPlants[1].list[1];
console.log(secondTree);
38. While Loops
>>Return to Menu
const myArray = [];
let i = 5;
while (i >= 0) {
myArray.push(i);
i--;
}
console.log(myArray);
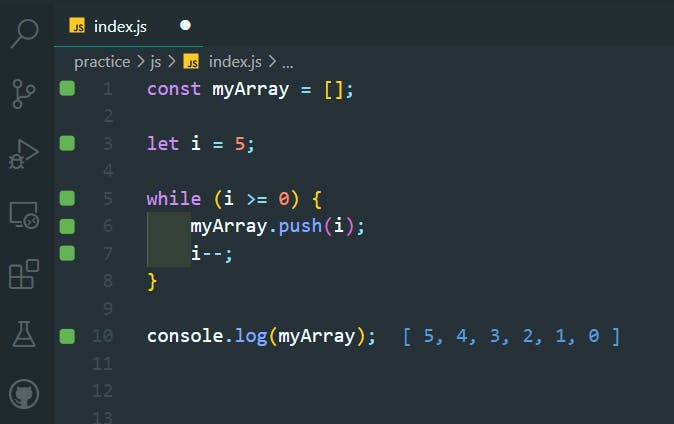
39. For Loops
>>Return to Menu
const myArray = [];
for (let i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
myArray.push(i);
}
console.log(myArray);
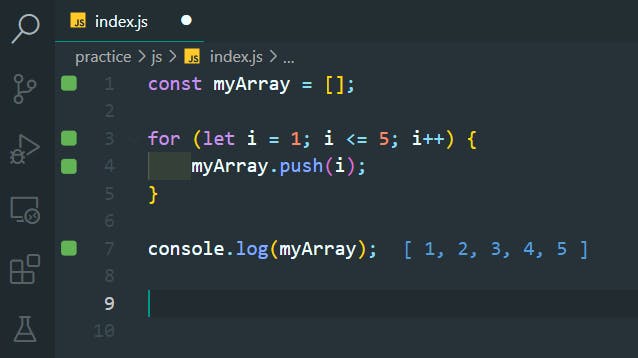
40. For Loops - Odd Numbers
>>Return to Menu
const myArray = [];
for (let i = 1; i < 10; i += 2) {
myArray.push(i);
}
console.log(myArray);
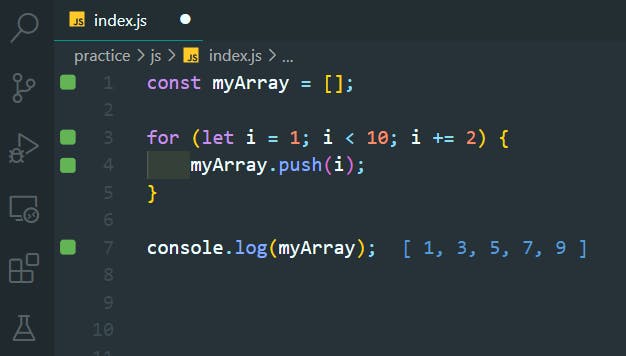
41. For Loops - Odd Numbers Backwards
>>Return to Menu
const myArray = [];
for (let i = 9; i > 0; i -= 2) {
myArray.push(i);
}
console.log(myArray);
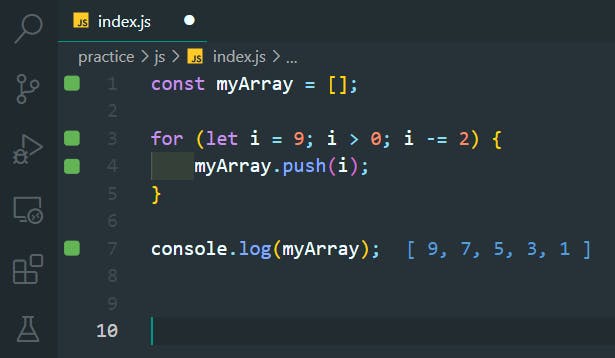
42. For Loops - Arrays
>>Return to Menu
const myArr = [2, 3, 4, 5, 6];
// Only change code below this line
let total = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < myArr.length; i++) {
total += myArr[i];
}
console.log(total);
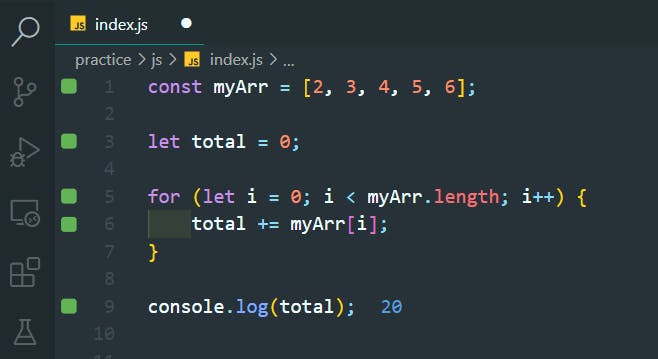
43. Nesting For Loops
>>Return to Menu
function multiplyAll(arr) {
let product = 1;
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < arr[i].length; j++) {
product *= arr[i][j];
}
}
return product;
}
console.log(multiplyAll([[1, 2],[3, 4],[5, 6, 7],]));
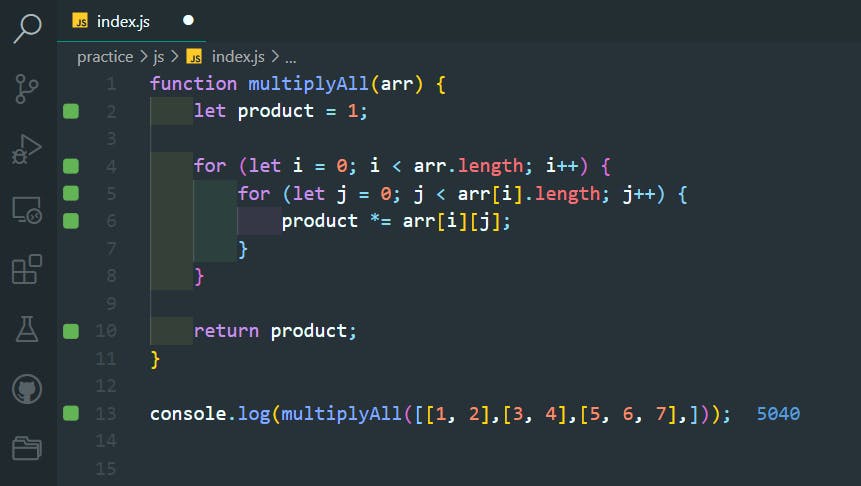
44. Do...While Loops
>>Return to Menu
const myArray = [];
let i = 10;
do {
myArray.push(i);
i++;
} while (i < 5);
console.log(myArray);
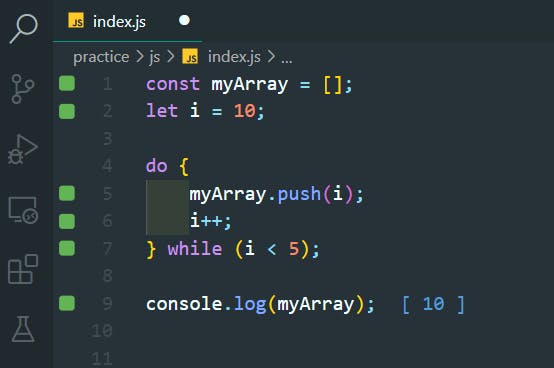
45. Recursions
>>Return to Menu
Product of first n numbers:
myArray = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7];
function multiply(arr, n) {
if (n <= 0) {
return 1;
} else {
return multiply(arr, n - 1) * arr[n - 1];
}
}
console.log(multiply(myArray, 3))
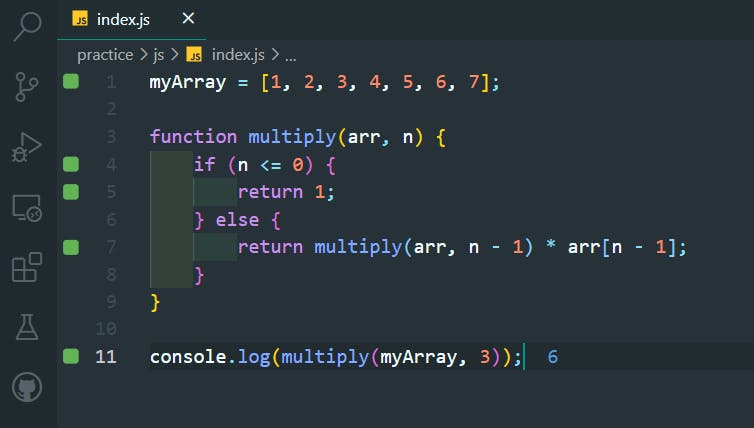
Sum of first n numbers:
myArray = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7];
function sum(arr, n) {
if (n <= 0) {
return 0;
} else {
return sum(arr, n - 1) + arr[n - 1];
}
}
console.log(sum(myArray, 4));
46. Generate Random Numbers
>>Return to Menu
function randomFraction() {
return Math.floor(Math.random() * 100);
}
console.log(randomFraction());
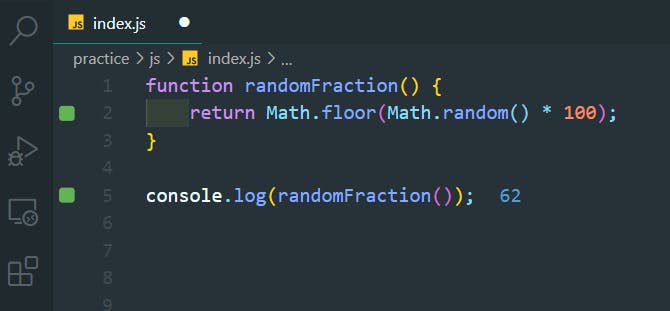
47. Generate Random Numbers within a Range
>>Return to Menu
Math.floor(Math.random() * (max - min + 1)) + min
function randomRange(myMin, myMax) {
return Math.floor(Math.random() * (myMax - myMin + 1)) + myMin;
}
console.log(randomRange(5, 20));
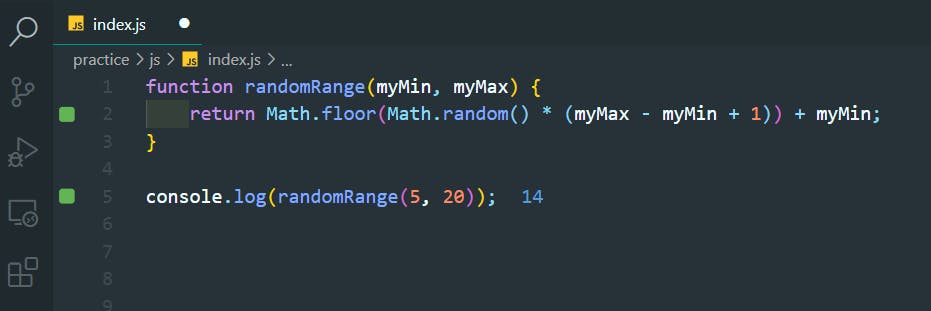
48. ParseInt Function
>>Return to Menu
const a = parseInt("007");
function convertToInteger(str) {
return parseInt(str);
}
console.log(convertToInteger("56"));
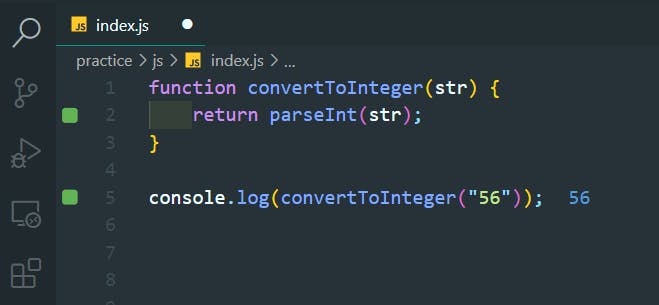
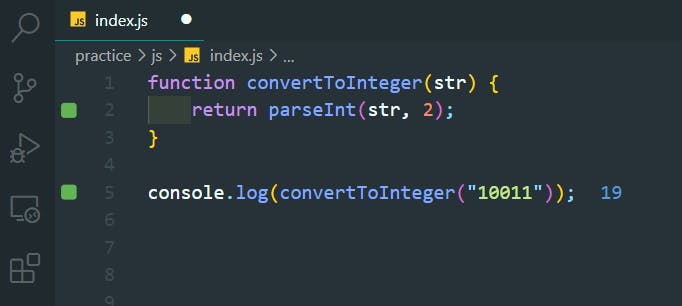
49. ParseInt Function with Radix
>>Return to Menu
- The parseInt() function parses a string and returns an integer.
- It takes a second argument for the radix, which specifies the base of the number in the string.
- The radix can be an integer between 2 and 36.
parseInt(string, radix);
- The radix variable says that 11 is in the binary system, or base 2.
- This example converts the string 11 to an integer 3.
const a = parseInt("11", 2);
function convertToInteger(str) {
return parseInt(str, 2);
}
console.log(convertToInteger("10011"));
50. Ternary Operator
>>Return to Menu
a ? b : c
- where a is the condition
- b is the code to run when the condition returns true
- c is the code to run when the condition returns false
function findGreater(a, b) {
return a > b ? "a is greater" : "b is greater or equal";
}
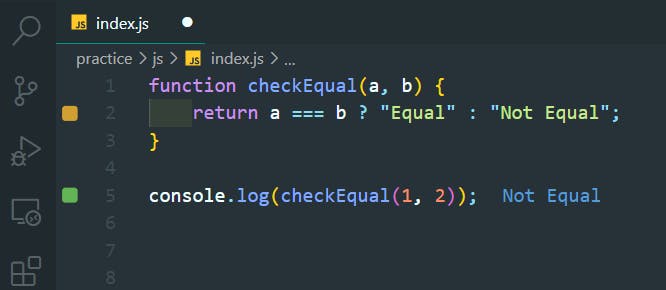
checkEqual function to check if two numbers are equal or not:
function checkEqual(a, b) {
return a === b ? "Equal" : "Not Equal";
}
console.log(checkEqual(1, 2));
51. Multiple Ternary Operators
>>Return to Menu
function findGreaterOrEqual(a, b) {
return (a === b) ? "a and b are equal"
: (a > b) ? "a is greater"
: "b is greater";
}
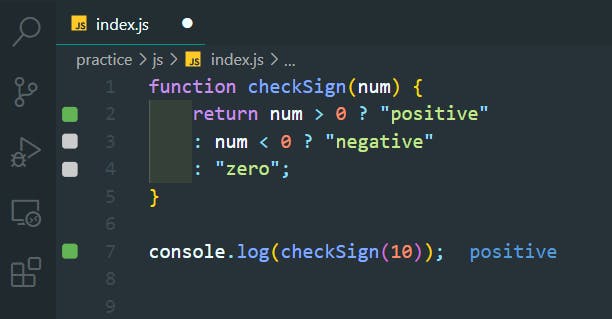
check if a number is positive, negative or zero:
function checkSign(num) {
return num > 0 ? "positive"
: num < 0 ? "negative"
: "zero";
}
console.log(checkSign(10));
52. Recursion for Countdown
>>Return to Menu
function countup(n) {
if (n < 1) {
return [];
} else {
const countArray = countup(n - 1);
countArray.push(n);
return countArray;
}
}
console.log(countup(5));
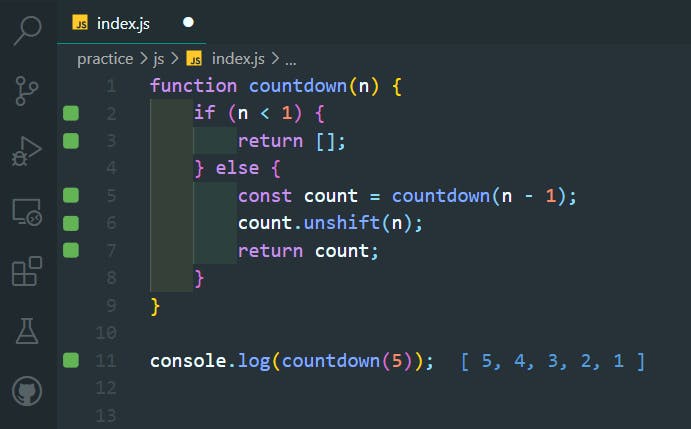
return the array [5, 4, 3, 2, 1]:
function countdown(n) {
if (n < 1) {
return [];
} else {
const count = countdown(n - 1);
count.unshift(n);
return count;
}
}
console.log(countdown(5));
53. Recursion for Range of Numbers
>>Return to Menu
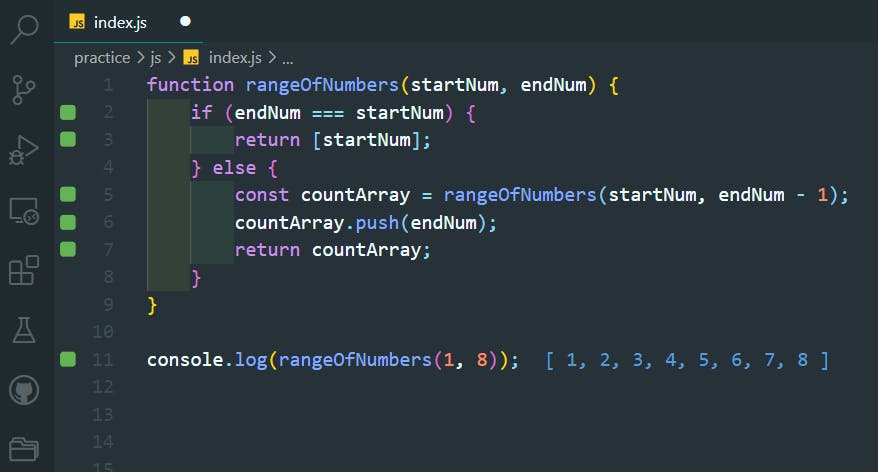
function rangeOfNumbers(startNum, endNum) {
if (endNum === startNum) {
return [startNum];
} else {
const countArray = rangeOfNumbers(startNum, endNum - 1);
countArray.push(endNum);
return countArray;
}
}
console.log(rangeOfNumbers(1, 8));
#End
Hope you enjoyed this! :) Follow me for more contents...
Get in Touch:
ifeanyiomeata.com
contact@ifeanyiomeata.com
Youtube: youtube.com/c/IfeanyiOmeata
Linkedin: linkedin.com/in/omeatai
Twitter: twitter.com/iomeata
Github: github.com/omeatai
Stackoverflow: stackoverflow.com/users/2689166/omeatai
Hashnode: hashnode.com/@omeatai
Medium: medium.com/@omeatai
© 2022

